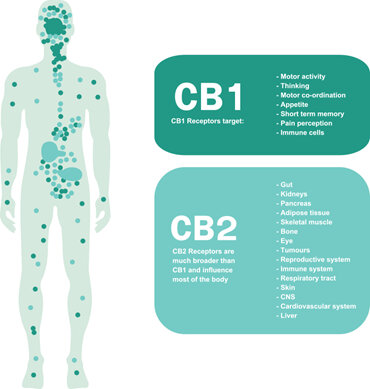
The human body has two main receptor types that bind (interact) with cannabinoids. CB1 and CB2. When cannabinoids bind to each of them they exert an effect. Depending on which cannabinoid binds to which receptor the outcomes vary.
In broad terms
CB1 recptors are concentrated in the Central Nervous System (CNS). The CNS is a cover all term that describes the brain and spinal cord. THC like bind to CB1 receptors slightly more than CB2 receptors
CB2 receptors are distributed around the body in organs, and are particularly associated with immue cells. CB2 receptors are found the CNS there aren't nearly as many as CB1.
Because CB1 recptors are found more typically in the CNS, and they have a great affinity for THC they tend to give CNS effects such as
- Reducing vomiting and nausea
- Releiving pain
- Stimulating appetite
- Supressing muscle spasm
THC is the molecule in cannabis that is psycho-active (gives you the high) so is associated with a feeling of well being - reduced anxiety
CB2 effects are much broader because of the wider distribution of CB2 recptors in different body tissues. These effects include
- Immune Supression
- Moderating neuropathic pain - e.g CRPS, Phantom Limb Pain
- Anti-inflammatory
There is also speculation about the presence of a CB3 receptor. The jury is still out on that.